Protein Model Quality Assessment User Guide
1: Introduction to the algorithm
Due to the diversity of computation-based protein structure prediction results, it is often essential to apply model quality assessment (MQA) to identify the most likely predicted structure(s) as the final output(s).
In this module, both single- and multi-model features are extracted from candidate structures, supplemented with structural homologs and our in-house inter-residue distance and orientation predictor. A deep graph neural network is then adopted to predict both per-residue and whole-protein quality assessment scores for each candidate structure.
2: Start to Use
2.1 Enter the amino acid sequence for prediction (required)
Edit amino acid sequence directly through the text box. The validity check of the input include:
1) It can only be entered in uppercase letters. Non-standard amino acid characters (ie: B, J, O, U, X, Z) are not supported.
2) The currently allowed amino acid sequence length ranges from 30 to 800 residues.
3) Only one sequence can be submitted at one time. The line beginning with '>' will be recognized as the sequence name and be ignored, and lines after this line will be regarded as the content of sequence; If there are multiple lines beginning with '>', multiple sequences will be recognized, which is not supported.

2.2 Upload candidate structure files locally (required)
Click the "Click to upload" button to upload one or multiple protein candidate structure files (in .pdb format).
The residue sequence in the candidate structure file must meet the amino acid sequence standard in 2.1 and be a sub sequence of the amino acid sequence uploaded in step 2.1.

2.3 Enter the task name (optional)
The user can also choose to enter the task name in the "Task Name" text box. If not entered, the website will use the randomly assigned UniqueID as the task name.
2.4 Submit task
After completing the above steps, click the "Predict" button. If "Your task has been created successfully!" is displayed, the submission is successful.
If the task is completed successfully, the user's registered mailbox will receive email of task completion notification. Usually, the calculation time of a task ranges from half an hour to several hours.
In order to allocate the limited resources reasonably, we limit the user's task quota. Hover the mouse over the "Submit" button to see the restriction and usage. The "Predict" button will be disabled when quota is insufficient.
3. Query the Result of Your Task
3.1 Query history
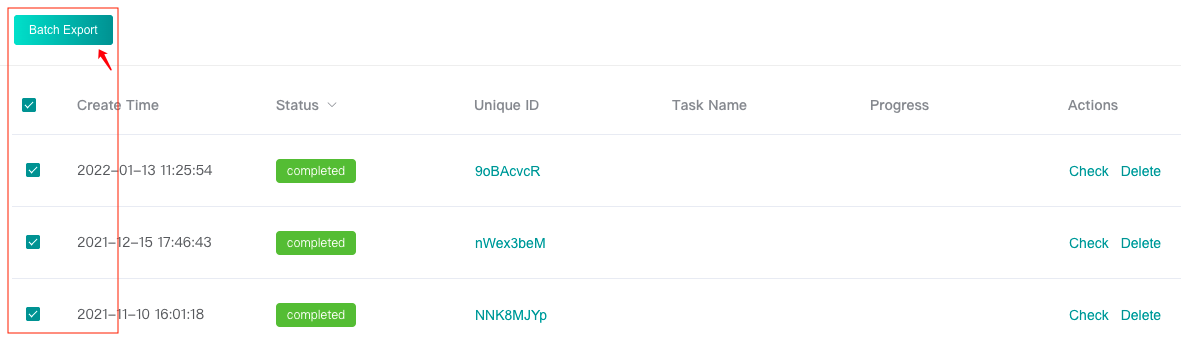
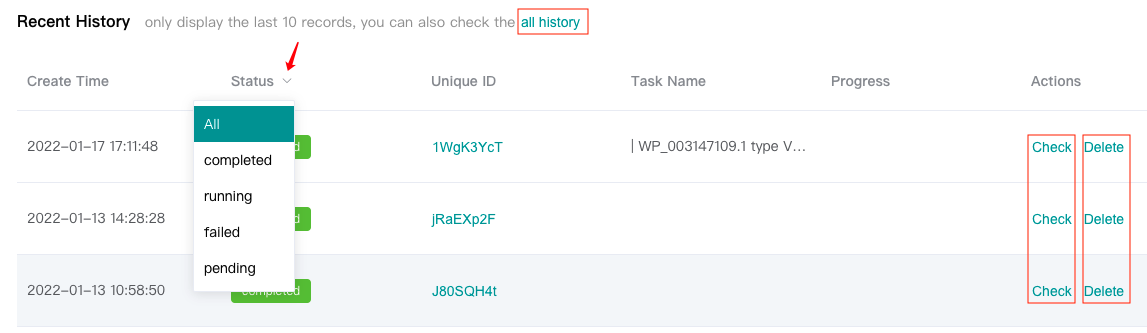
Users can view the "Recent History" below, which only displays the last 10 history records, or click the "all history" to see all history records.
Users can "Check" completed tasks (marked in green).
Users can "Delete" completed or failed or pending tasks. Tasks in running status can not be deleted.
Click the drop-down arrow next to "Status" to filter according to the task running status.
3.2 Query results
Click the "Check" button on the history records to view the task results.
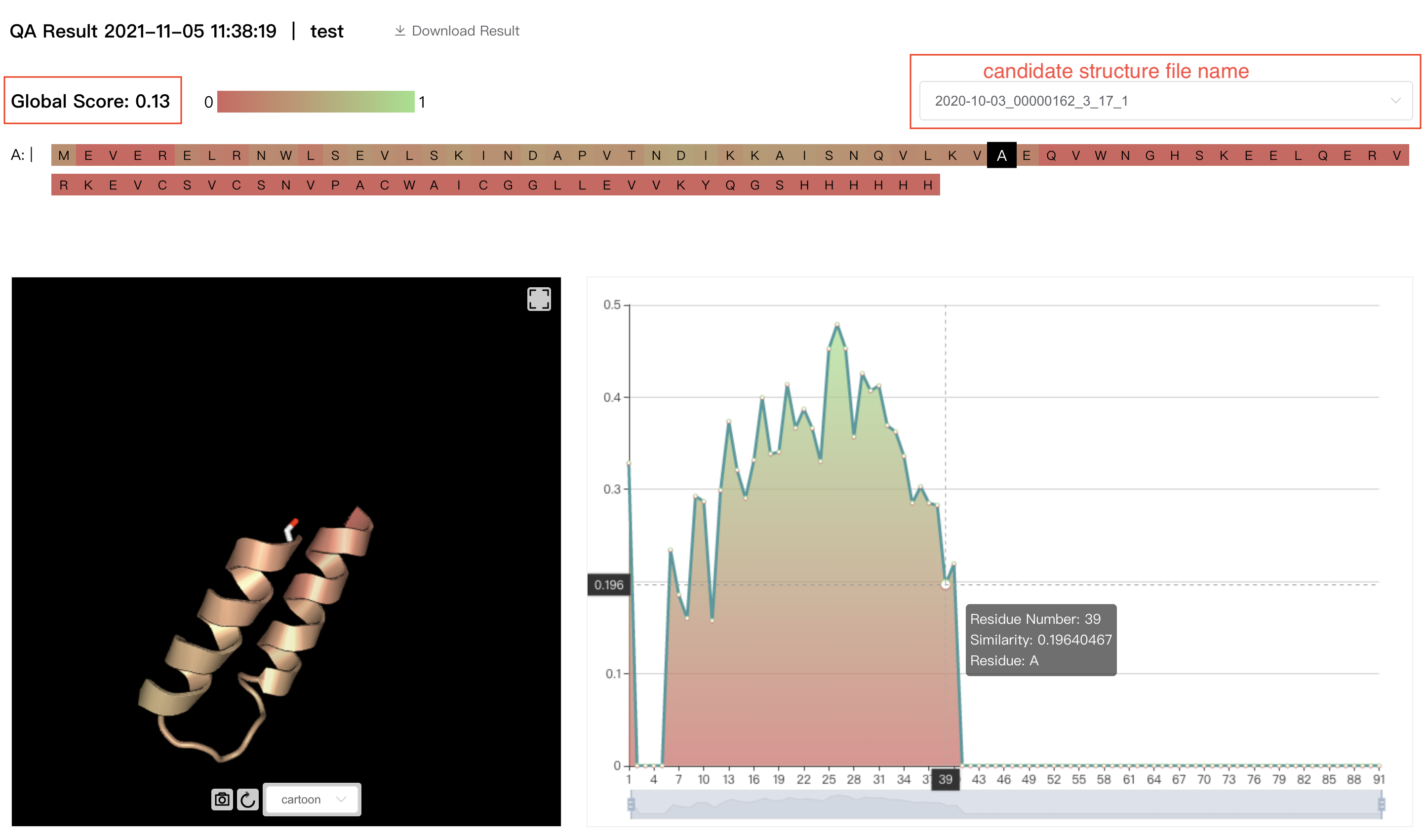
The result interface displays:
-
The amino acid sequence. Select one residue to show the details.
-
The file names of candidate structure files. Choose one file and the results of this file will be displayed on the interface.
-
The 3D image of the candidate structure.
-
The "Global Score" of the candidate structure which represents the average score of all residues in this structure, and the predicted scores of each residue in the candidate structure. A residue with a score of zero indicates that this candidate structure does not contain this residue, which affects "Global Score".
3.3 Download results
-
Click "Download Result" to download the result file of one task in the result interface:
-
Download task results in batches in the history page: